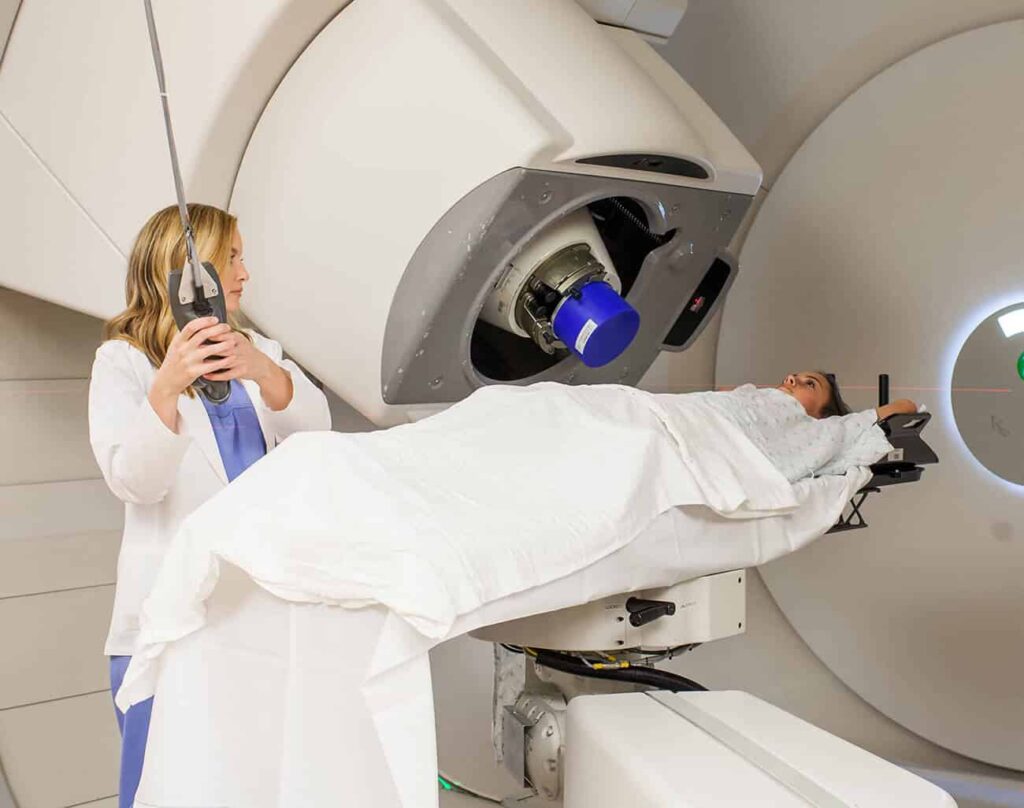
ABOUT BREAST CANCER TREATMENT
Approximately one in eight women will be diagnosed with breast cancer at some point in their lives. While traditional radiation treatments like IMRT and TomoTherapy can effectively treat breast cancer, they often cause side effects due to excess radiation exposure. Proton therapy offers a solution by reducing this risk, as protons can be precisely stopped within the tumor.
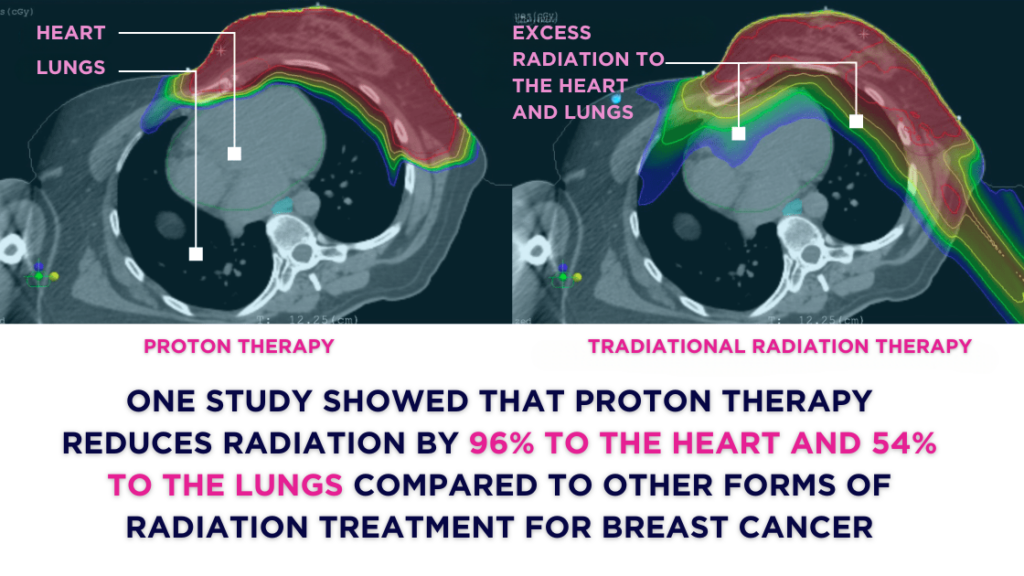
Studies have shown that proton therapy can significantly reduce radiation exposure to the heart and lungs. For left-sided breast cancer, proton therapy reduces the mean heart dose by approximately 50-70% compared to traditional X-ray radiation therapy.
Benefits of proton therapy
Precision targeting
Proton therapy’s ability to stop precisely within the tumor minimizes radiation exposure to surrounding healthy tissues and critical structures, such as the heart and lungs.
Reduced side Effects
Quality of life
Am I a candidate for proton therapy?
Proton therapy is available for patients with early-stage and locally advanced breast cancers, including ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS), inflammatory breast cancer, ER/PR positive or negative, Her2Neu positive or negative, triple-positive or triple-negative breast cancer. It is also beneficial for patients who have previously received radiation therapy and for those who are concerned about the potential long-term effects of radiation. Proton therapy is often recommended for:
- Patients with left-sided breast cancer, where the heart is at greater risk of radiation exposure.
- Patients with tumors close to the chest wall or near other critical structures.
- Young patients, due to the reduced risk of secondary cancers and long-term side effects.
- Patients with genetic predispositions that increase sensitivity to radiation.
PROTON THERAPY HAS PROVEN CLINICAL RESULTS
Treatment Process for Proton Therapy for Breast Cancer

Breast Cancer
WHy We're Different

Frequently Asked Questions
FIND OUT IF PROTON THERAPY IS RIGHT FOR YOU
"*" indicates required fields
FAQs
Why do I need radiation therapy after breast surgery?
Radiation therapy is commonly recommended after breast-conserving surgery (lumpectomy) to destroy any microscopic cancer cells that might remain in the breast or surrounding tissues. It may also be used after a mastectomy if the cancer was large or involved the lymph nodes.
What are the different types of radiation therapy for breast cancer?
The main types of radiation therapy for breast cancer include:
- External Beam Radiation Therapy (EBRT): The most common type, where a machine directs radiation beams at the breast from outside the body. Proton Therapy is a type of EBRT.
- Internal Radiation (Brachytherapy): A less common type, where radioactive seeds or pellets are placed inside the breast tissue near the tumor site.
- Intraoperative Radiation Therapy (IORT): Radiation is delivered directly to the tumor bed during surgery.
What is proton therapy and how does it work?
Proton therapy is a type of radiation treatment that uses protons instead of traditional X-rays to treat cancer. Protons are positively charged particles that can be precisely controlled to release their energy directly at the tumor site, minimizing damage to surrounding healthy tissues.
How is proton therapy different from traditional radiation therapy?
The key difference between proton therapy and traditional radiation therapy (using X-rays) is the precision of proton therapy. Protons can be targeted more accurately, delivering maximum radiation to the tumor while sparing surrounding healthy tissues and vital organs such as the heart and lungs.
What are the benefits of proton therapy for breast cancer?
The benefits of proton therapy for breast cancer include:
- Reduced Radiation Exposure: Less radiation to healthy tissues and critical organs.
- Fewer Side Effects: Lower risk of side effects such as skin irritation, fatigue, and damage to the heart and lungs.
- Improved Quality of Life: Better overall quality of life during and after treatment due to fewer side effects.
- Lower Risk of Secondary Cancers: Reduced risk of developing secondary cancers due to less radiation exposure to healthy tissues.
Who is a candidate for proton therapy?
Proton therapy is suitable for many breast cancer patients, especially those with:
- Tumors located near critical structures like the heart or lungs.
- Left-sided breast cancer, where the heart is at greater risk.
- Previous radiation therapy patients.
- Younger patients concerned about long-term side effects.
- Patients with genetic predispositions increasing sensitivity to radiation.
What can I expect during proton therapy treatment?
The treatment process includes:
- Consultation: Initial visit with a radiation oncologist specializing in proton therapy.
- Planning: Advanced imaging techniques (CT, MRI) are used to create a 3D model of the tumor and surrounding tissues.
- Simulation: A session to map the treatment area and ensure accurate targeting.
- Treatment Sessions: Typically conducted 5 days a week for several weeks. Each session lasts about 15-30 minutes, during which patients lie on a treatment table while protons are delivered to the tumor.
Can proton therapy be combined with other treatments?
Yes, proton therapy can be part of a comprehensive treatment plan that includes surgery, chemotherapy, hormone therapy, or targeted therapy. Your oncologist will determine the best combination based on your specific case.
How long is a course of proton therapy?
The duration of proton therapy for breast cancer varies, but a typical course lasts about 3 to 6 weeks, with treatments given once a day, 5 days a week. Some patients may be candidates for shorter courses or hypofractionated radiation, which delivers higher doses over a shorter period.
Will proton therapy affect my daily life?
Proton therapy is usually well-tolerated, allowing many patients to continue their normal activities. However, some adjustments may be needed to manage side effects such as fatigue. It's important to listen to your body and rest as needed.
How do I manage the side effects of proton therapy?
Managing side effects involves:
- Skin Care: Use gentle skincare products and avoid sun exposure to the treated area.
- Rest: Prioritize rest to combat fatigue.
- Hydration and Nutrition: Maintain a healthy diet and stay hydrated.
- Exercise: Engage in light physical activity to help reduce fatigue.
Is proton therapy covered by insurance?
Coverage for proton therapy varies by insurance provider and plan. It's important to check with your insurance company to understand your coverage and any out-of-pocket costs. Your healthcare team can assist with insurance approval and financial counseling.
What follow-up care is needed after proton therapy?
Regular follow-up visits are scheduled to monitor your progress, manage any side effects, and ensure the effectiveness of the treatment. These visits are crucial for long-term health and detecting any recurrence early.
